Let’s continue working on our “Simplest TensorFlow example” series. In this post, I thought of coding up KNN algorithm, which is a really simple non-parametric classification algorithm. Not going into the details, but the idea is just memorize the entire training data and in testing time, return the label based on the labels of “k” points closest to the query point. <br > Given the simplicity of algorithm, it is a perfect candidate to just try to implement in tensorflow.
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
%matplotlib inline
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.style.use('ggplot')
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (20.0, 10.0)
We create synthetic data
num_points_each_cluster = 100
mu1 = [-0.4, 3]
covar1 = [[1.3,0],[0,1]]
mu2 = [0.5, 0.75]
covar2 = [[2.2,1.2],[1.8,2.1]]
X1 = np.random.multivariate_normal(mu1, covar1, num_points_each_cluster)
X2 = np.random.multivariate_normal(mu2, covar2, num_points_each_cluster)
y1 = np.ones(num_points_each_cluster)
y2 = np.zeros(num_points_each_cluster)
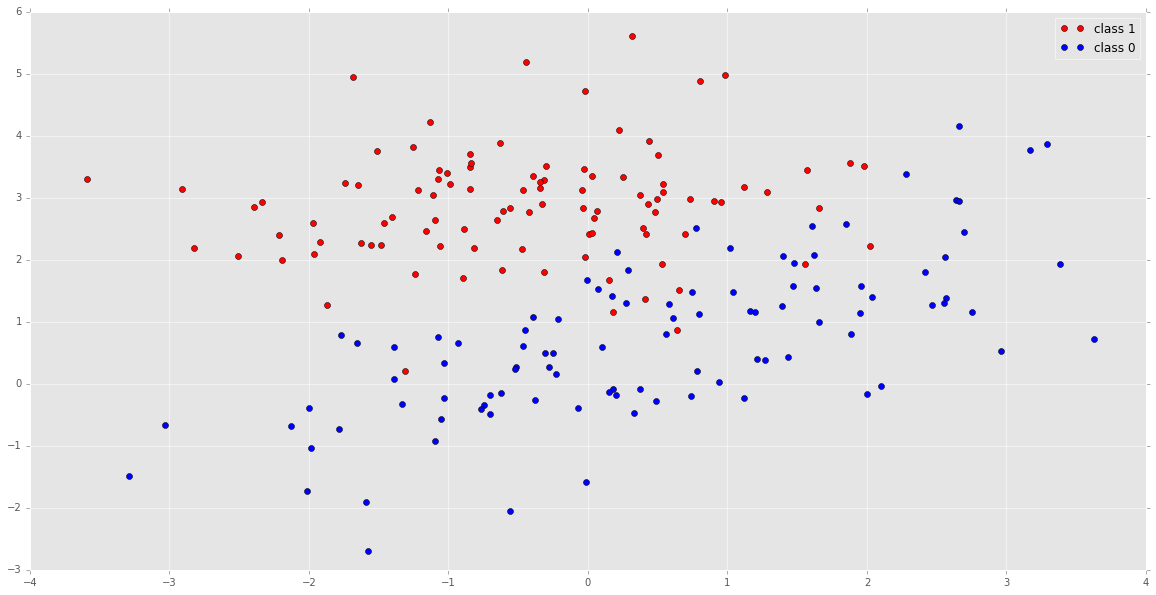
Let’s visualize this data
plt.plot( X1[:, 0], X1[:,1], 'ro', label='class 1')
plt.plot(X2[:, 0], X2[:,1], 'bo', label='class 0')
plt.legend(loc='best')
plt.show()
X = np.vstack((X1, X2))
y = np.hstack((y1, y2))
print X.shape, y.shape
(200, 2) (200,)
X_tf = tf.constant(X)
y_tf = tf.constant(y)
Main logic for KNN
def predict(X_t, y_t, x_t, k_t):
neg_one = tf.constant(-1.0, dtype=tf.float64)
# we compute the L-1 distance
distances = tf.reduce_sum(tf.abs(tf.subtract(X_t, x_t)), 1)
# to find the nearest points, we find the farthest points based on negative distances
# we need this trick because tensorflow has top_k api and no closest_k or reverse=True api
neg_distances = tf.multiply(distances, neg_one)
# get the indices
vals, indx = tf.nn.top_k(neg_distances, k_t)
# slice the labels of these points
y_s = tf.gather(y_t, indx)
return y_s
def get_label(preds):
counts = np.bincount(preds.astype('int64'))
return np.argmax(counts)
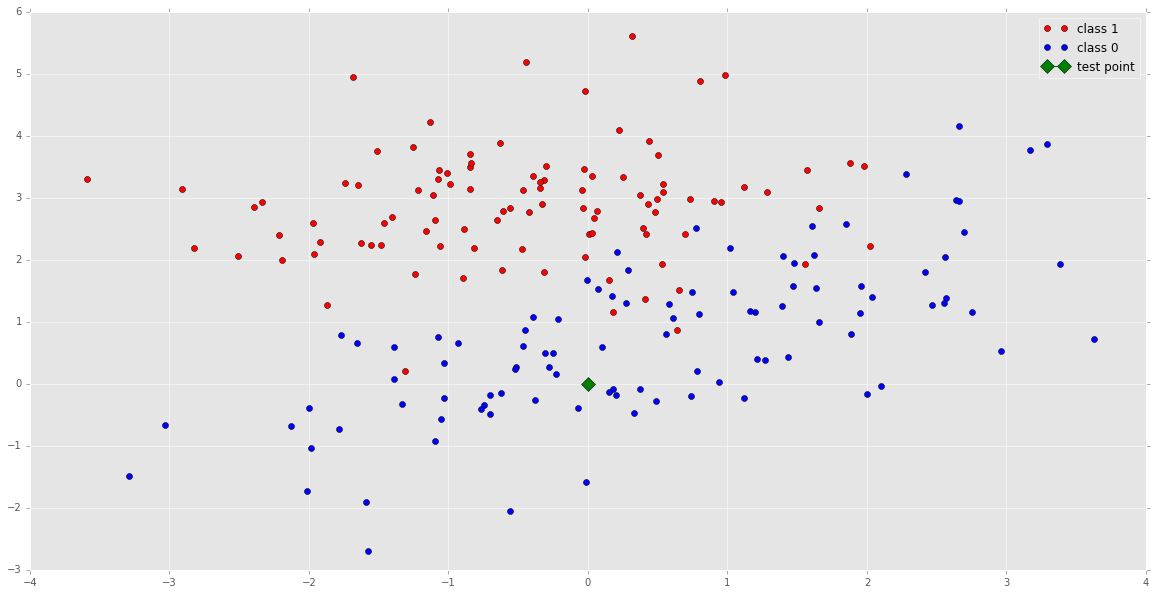
Generate a test point
example = np.array([0, 0])
example_tf = tf.constant(example,dtype=tf.float64)
plt.plot( X1[:, 0], X1[:,1], 'ro', label='class 1')
plt.plot(X2[:, 0], X2[:,1], 'bo', label='class 0')
plt.plot(example[0], example[1], 'g', marker='D', markersize=10, label='test point')
plt.legend(loc='best')
plt.show()
k_tf = tf.constant(3)
pr = predict(X_tf, y_tf, example_tf, k_tf)
sess = tf.Session()
y_index = sess.run(pr)
print get_label(y_index)
0
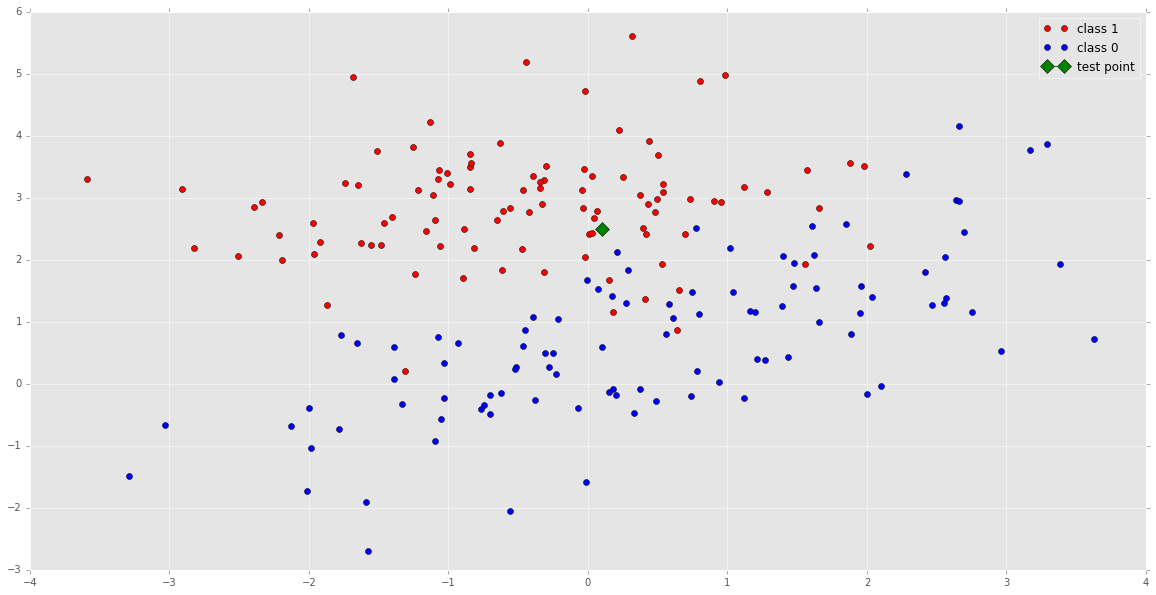
example_2 = np.array([0.1, 2.5])
example_2_tf = tf.constant(example_2)
plt.plot( X1[:, 0], X1[:,1], 'ro', label='class 1')
plt.plot(X2[:, 0], X2[:,1], 'bo', label='class 0')
plt.plot(example_2[0], example_2[1], 'g', marker='D', markersize=10, label='test point')
plt.legend(loc='best')
plt.show()
pr = predict(X_tf, y_tf, example_2_tf, k_tf)
y_index = sess.run(pr)
print get_label(y_index)
1